Sorbents Drying equipment
Veolite Drying cabinet
GlobeCore has developed and is about to begin serial production of a new product designed for removal of water from granulated sorbents like zeolite and silica gel. Both are widely used for transformer oil purification

This system can be used by facilities which use zeolites for deep dehydration of transformer oil. Such dehydration requires sorbents with granule size of at least 1 mm. The system can also be used in other fields: any application which requires heating, tempering, baking of materials or parts.
Specifications and general principle of operation
The cabinet is a welded frame covered by metal sheets, the metal being Steel3. TGhe unit is supplied with mesh pans and a frame to install them. A vent is installed in the chamber to remove gas products of thermal treatment. The cabinet is heated by electric tube heaters installed in the side air conduits of the chamber. Max heating temperature is 400oC. The unit is equipped with circulation fan, which allows uniform distribution of heat across all sorbent layers. Air intake is in the upper part of the unit, from there the air goes to the grate in the bottom of the chamber (upward motion). An automatic temperature control system adjustable from the control panel maintains temperature within ± 9 degrees. A timer allows heating and tempering for a set duration. for better insulation, the gap between the door and the chamber’s front side is sealed with a bazalt cord.
The unit connects to AC grid, 380V, 50 Hz by a 5*10 or 4*10 PE cable. The heaters are protected from short circuit currents by an automatic breaker.
Th eunit is controlled from the control panel located on the side of the device.
|
No |
Item |
Value |
|
1 |
Zeolite load, dm3 |
130 |
|
2 |
Number of pans |
10 |
|
3 |
Rated heater power, kW |
14,4 |
|
4 |
Temperature adjustment range, °C |
40…400 |
|
5 |
Number of electric heaters А16 1.6 kW Т 220V |
9 |
|
6 |
Voltage at 50 Hz, V |
380 |
|
7 |
Empty weight, kg |
550±10% |
|
8 |
Dimensions, mm – length – width – height |
1440 1060 1660 |
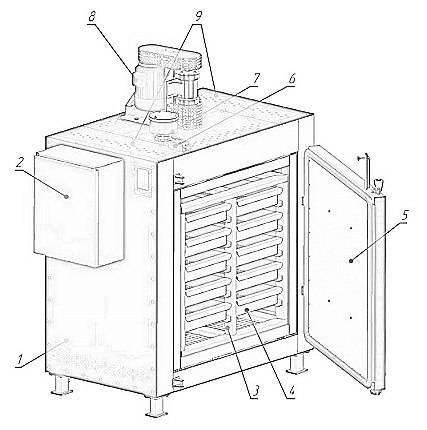
General station view: 1 – body; 2 – control panel; 3 – chamber with fram for pan installation; 4 – pan; 5 – door; 6 – safety switch; 7 – exhaust; 8 – circulation fan; 9 – heater terminal covers.
The cabinet is designed for dessication of both natural and synthetic zeolite (depending on the type, heating temperature is changed to match specifications).
Zeolite applications:
- Deep dessication of gas flow
- natural has
- oil gas
- process and instrument air
- reformer and cracking gas
- multiple glass pane
- package and container internal space
- pyrolysis gas in ethylene production
Purification of gas flows:
- removal of native sulphur compounds, carbon dioxide and mercaptans from natural gas
- removal of sulphur compounds, carbon dioxide and mercaptans from oil gas
- removal of carbon dioxide from air before separation to oxigen and nitrogen
- short cycle adsorbtion method of oxygen production
- purification and drying of biogas
- removal of dioxins from waste processing plant gases
- removal of radionuclides, sulphur and nitrogen compounds from exit gas
- purification of smelt and creation of protective environments in metallurgy
Deep dessication of liquids
- drying and regeneration of transformer oils
- drying and regeneration of freon oil cooling agents in refrigerators
- filters for drying and regeneration of motor oils
- filter for drying of diesel and gasoline fuel, dump truck hydraulics
- concentration of alcohol solutions
- purification of organic liquids (kerosene, hexane, benzol, hexahydrobenzene, methanol, ethanol, isopropanol etc)
Molecular sieves (separation of materials depending on molecule size) – separation of hydrocarbons of different structure:
- extraction and purification of normal paraffin hydrocarbons, which serve as feedstock for detergent and protein-vitamin component production
- separation of oleffin and paraffin hydrocarbons
- separation of aromatic hydrocarbons (mixed xylols and ethyl benzene)
Cationic exchange media (separation by ion exchange) – water deionization, removal of heavy metal ions and radionuclides in atomic energy:
- purification of galvanic waste in machine construction
- removal of radionuclides from liquid waste of nuclear power plants
- water deionization in boilers
- process water deionization
Chemical reaction catalysis:
- kerosene and gas oil fraction cracking
- production of motor fuels from oleffin gases (high octane gasolene and diesel fuel)
- conversion of methanol to motor fuel
- cyclization of propane and butane (allows production of naphthenic and aromatic hydrocarbons, a valuable petrochemical material) afterburning of vehicle exit and exhaust gases to CO2 and H2O
